Intermittent fasting has gained popularity among athletes due to its potential benefits for improving performance and body composition. This article examines the potential benefits and risks of incorporating intermittent fasting into an athlete’s training regimen.
Understanding Intermittent Fasting in Sports
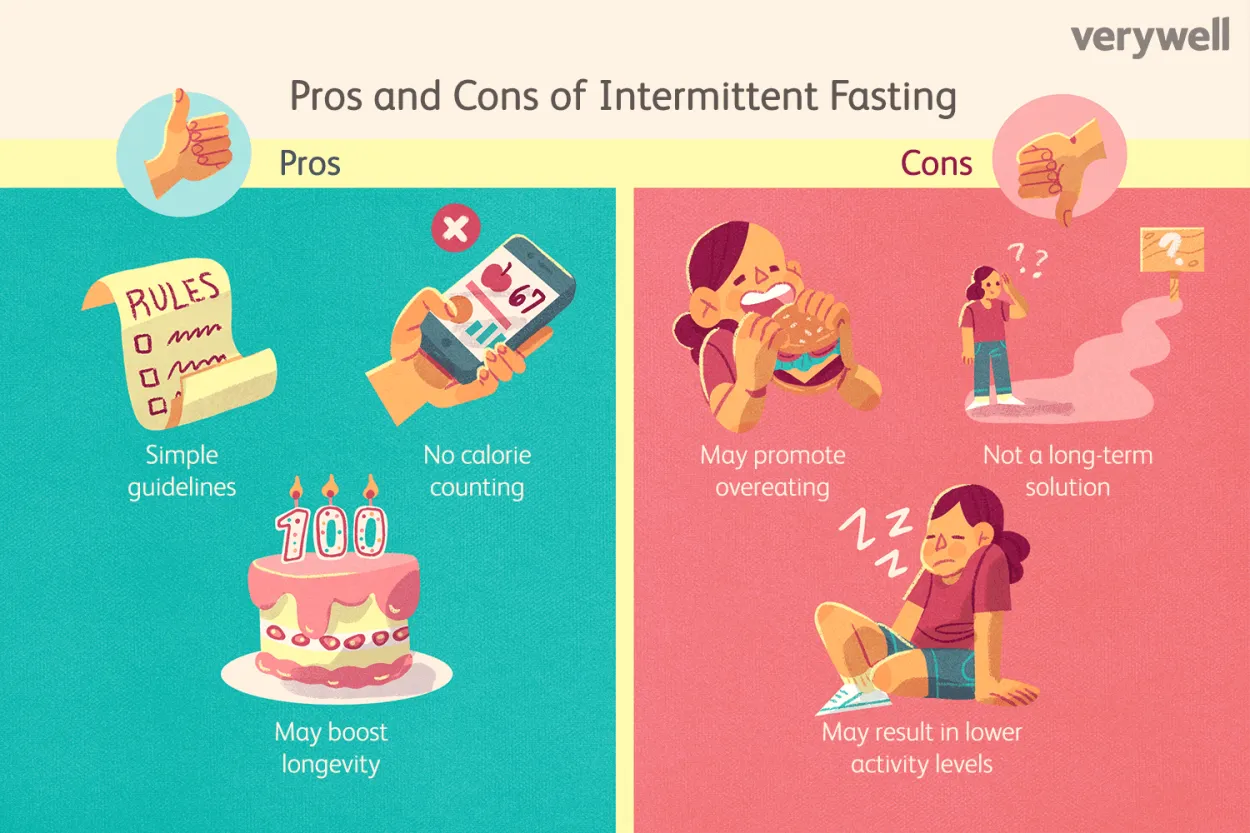
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity in recent years as a dietary approach that involves cycling between periods of fasting and eating. While it has been mostly associated with weight loss and improved metabolic health, athletes have also started exploring the potential benefits and risks of intermittent fasting in relation to their performance.
Potential Benefits:
- Enhanced fat burning: Intermittent fasting may increase the body’s ability to burn stored fat for energy during workouts, which can be beneficial for athletes aiming to reduce body fat percentage.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: By promoting better insulin sensitivity, intermittent fasting can help athletes optimize their body’s ability to utilize carbohydrates effectively, leading to improved energy levels and endurance.
- Enhanced autophagy: Fasting triggers a cellular cleaning process called autophagy, which may promote tissue repair and rejuvenation, potentially reducing the risk of injury and speeding up recovery.
- Inflammation reduction: Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may help reduce chronic low-grade inflammation, which is often associated with intense training and athletic performance.
Potential Risks:
- Decreased muscle mass: Extended periods of fasting can potentially lead to muscle breakdown, which is undesirable for athletes striving to maintain or increase muscle mass.
- Energy and performance fluctuations: Adjusting to intermittent fasting can initially cause fluctuations in energy levels and athletic performance. It may take time for the body to adapt and find optimal performance during fasting periods.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Fasting for extended periods of time may increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies, especially if inadequate dietary choices are made during eating windows.
- Potential hormonal imbalances: Intermittent fasting can affect hormone levels, and for female athletes, this may potentially disrupt the menstrual cycle and hormone-driven processes critical for performance.
In Conclusion
While intermittent fasting may offer some potential benefits for athletes, it is important to consider individual differences, training goals, and consult with a healthcare professional or sports nutritionist before embarking on an intermittent fasting protocol. The effects of intermittent fasting can vary greatly between individuals, and careful monitoring of performance, recovery, and overall well-being should be prioritized.
Balancing Training and Fasting Schedules
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity in recent years as a method for weight loss and improved health. However, for athletes who rely on proper nutrition to fuel their performance, finding the right balance between training and fasting schedules is crucial.
While intermittent fasting may offer some benefits, such as improved insulin sensitivity and increased fat burning, it can also present challenges for athletes. One of the main concerns is the potential impact on energy levels during training sessions.
Athletes who engage in intense workouts require an adequate supply of carbohydrates and protein to optimize their performance and facilitate muscle recovery. Fasting for extended periods, especially during the fasting window, may limit the availability of these essential nutrients. As a result, athletes may experience decreased energy, reduced strength, and impaired recovery.
To ensure a successful integration of intermittent fasting into an athlete’s routine, it is crucial to carefully plan training and fasting schedules. Here are a few key considerations:
- Timing: Schedule your training sessions during the eating window or closer to when you break your fast. This allows you to fuel your body adequately before and after workouts.
- Nutrient-dense meals: Focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods during your eating window to meet your energy and nutrient needs. Include a balance of carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated throughout the fasting period and during training sessions. Drink water and electrolyte-rich fluids to maintain optimal performance.
- Recovery: Pay attention to post-workout nutrition to support muscle recovery and replenish glycogen stores. Consider consuming a mix of carbohydrates and protein within the eating window following intense training sessions.
- Individualization: Every athlete is different, and what works for one may not work for another. Experiment with different fasting and training schedules to find the approach that best suits your needs and goals.
It’s important to note that successful implementation of intermittent fasting for athletes depends on factors such as training intensity, duration, and overall calorie and nutrient needs. Consulting with a sports nutritionist or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and help ensure you maintain optimal performance while incorporating intermittent fasting into your routine.
Nutritional Considerations During Fasting
Fasting, especially intermittent fasting, has gained popularity among athletes for its potential benefits in enhancing performance and overall well-being. However, it is important for athletes to consider their nutritional needs during fasting to optimize their training and recovery.
Hydration
Staying properly hydrated is essential during fasting periods. Athletes should focus on consuming sufficient fluids to prevent dehydration and maintain optimal performance. Water, herbal teas, and non-caloric beverages can help fulfill hydration needs.
Macronutrient Distribution
Adequate consumption of macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, is crucial for athletes during fasting. It is recommended to adjust macronutrient distribution to ensure sufficient energy availability and muscle protein synthesis. Consulting with a registered dietitian can be beneficial in determining the appropriate ratios.
Nutrient Timing
Timing of nutrient intake becomes crucial when practicing intermittent fasting. Athletes may want to schedule their workouts and meal times strategically to optimize performance and recovery. Consuming a balanced meal containing carbohydrates and proteins shortly after a workout can facilitate muscle glycogen replenishment and muscle repair.
Micronutrient Intake
Athletes should pay attention to their micronutrient intake during fasting to avoid any deficiencies. Including a variety of nutrient-dense fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help meet these needs. If necessary, supplementation may also be considered, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Listen to Your Body
Every athlete is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. It is important to listen to your body during fasting and make adjustments accordingly. Pay attention to hunger cues, energy levels, and overall well-being, and make any necessary modifications to ensure your nutritional needs are met.
Overall, while intermittent fasting can potentially offer benefits for athletes, it is crucial to prioritize nutritional considerations during fasting. By maintaining proper hydration, adjusting macronutrient distribution, considering nutrient timing, ensuring adequate intake of micronutrients, and listening to your body, athletes can make the most of their fasting practice while supporting their performance and overall health.
The Impact of Fasting on Athletic Performance
Fasting, specifically intermittent fasting, has gained popularity in recent years as a potential strategy for improving athletic performance. This form of fasting involves alternating periods of fasting and eating within a certain timeframe.
One potential benefit of intermittent fasting for athletes is improved insulin sensitivity. When we fast, our insulin levels decrease, which may help our bodies become more efficient at utilizing stored fat for energy. This can be particularly beneficial for endurance athletes, as they rely heavily on their fat stores during long periods of exercise.
Fasting has also been shown to enhance cellular repair and regeneration processes. During fasting, autophagy, a natural process where damaged cells are removed and replaced with new ones, is upregulated. This can aid in recovery from intense training sessions, reducing inflammation and the risk of injury.
On the other hand, fasting may pose some risks to athletes. Restricting calorie intake for extended periods can lead to inadequate energy availability, which may negatively impact performance and recovery. It is crucial for athletes to ensure they still consume enough nutrients and calories to support their training and overall health.
Individual responses to fasting can vary, and it is important for athletes to experiment and find the approach that works best for them. Consulting with a sports nutritionist or dietitian can provide valuable guidance in implementing intermittent fasting safely and effectively.
Personal Experiences with Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity in recent years, not only among the general population but also among athletes. Many athletes have embraced this eating pattern in the hopes of improving their performance and achieving their fitness goals. While the effects of intermittent fasting can vary from person to person, here are some personal experiences shared by athletes who have tried it:
-
Increased Energy Levels
Several athletes reported experiencing increased energy levels while practicing intermittent fasting. They found that by giving their bodies a break from constant digestion, they had more energy available for their workouts and training sessions.
-
Improved Focus
Intermittent fasting has also been associated with improved mental clarity and focus. Athletes mentioned that they felt more alert and focused during their workouts, which allowed them to push themselves harder and achieve better results.
-
Better Fat Loss
Many athletes who incorporated intermittent fasting into their routines noticed a reduction in body fat percentage. This could be attributed to the extended periods of fasting, as it promotes the use of stored fat as a source of energy.
-
Enhanced Recovery
Some athletes found that intermittent fasting improved their recovery time after intense training sessions. They reported reduced muscle soreness and faster muscle repair, allowing them to bounce back quicker and continue training at high intensities.
It’s important to note that these personal experiences may not apply to everyone. Athletes interested in trying intermittent fasting should consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine if it is suitable for their individual needs and goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intermittent fasting can potentially offer several benefits for athletes, such as improved insulin sensitivity, fat oxidation, and cellular repair. However, it is crucial to consider individual needs, training demands, and consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist to ensure it fits within an athlete’s overall nutrition and performance goals.